Reinventing Healthcare with Artificial Intelligence
By Sunil Kakade, Director Information Architecture & Dr. Umar Iqbal, CMIO, Dignity Health
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare is likely to evolve at a more rapid pace than any other type of technological advancement. AI thrives on data. Currently, the healthcare industry is experiencing an explosion of data, owing to the digitization of medical records and patient-generated information making the industry an epicenter of AI-driven innovation. While all industries will benefit from AI, the healthcare sector is poised to benefit the most as it will directly create an impact on humanity by improving the quality of life.
With a focus on improving patient outcomes, provider experience, and business performance, usage of AI in healthcare is rapidly increasing. A recent report published by CBInsights shows that AI startups have raised $4.3B across 576 deals in the private market.
AI applications hold promise to reshape all facets of the healthcare industry – from speedy drug discovery, predicting diagnosis faster, detection of claims fraud, to improving resource utilization and saving lives. This article discusses the fundamentals of artificial intelligence technology, reviews various applications and concludes with best practices for the adoption of AI in healthcare enterprises.
The Artificial Intelligence Ecosystem
 Human intelligence is a collection of cognitive abilities such as listening, perceiving, learning, smelling, sensing, reasoning and decisions-making. Fundamentally AI holds the capability to perform intelligent human behavior by learning, reasoning, solving problems, and predicting outcomes using algorithms that simulate human cognitive capabilities.
Human intelligence is a collection of cognitive abilities such as listening, perceiving, learning, smelling, sensing, reasoning and decisions-making. Fundamentally AI holds the capability to perform intelligent human behavior by learning, reasoning, solving problems, and predicting outcomes using algorithms that simulate human cognitive capabilities.
However, AI is not a single technology or algorithm rather it’s a collection of various technologies that include a big data platform, and algorithms that learn from data, ultimately creating AI models and workflow integration techniques that infer intelligent decisions from models at the point of care. The following section outlines the core components of the AI ecosystem.
Big data is a term that refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing technologies. Relative to other industries the volume of data in healthcare is smaller but can be extraordinarily complex. In healthcare, the big data system must have the ability to store and process medical data that includes images, medical notes, genomics, sensor, and electronic patient records and combine it with various operations and payment data.
Al Algorithms are a set of mathematical methods that automate human behavior based on data. These algorithms interpret images, predict outcomes, generate recommendations and discover unknowns based on similarities and anomalies across the patient population.
Workflow integration is the key element for the success of any AI healthcare program. This is where Physicians and Nurses spend a great deal of time and the place where precious time can be saved and key decisions can be influenced. It enables augmentation of intelligence from AI at the point of care. One of the most effective techniques to make the integration of AI in EMR feasible is SMART ON FHIR.
Artificial Intelligence Methods
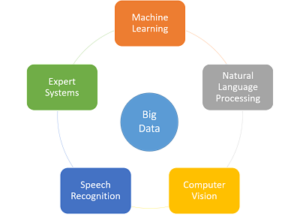 Human intelligence abilities such as listening, seeing, smelling, sensing, learning, reasoning and decision-making can be created by machines using various AI intelligence methods. In the world of healthcare, professionals can augment intelligence created by AI to improve the accuracy of diagnosis, predict outcomes, and recommend more effective care paths by detecting hidden and known patterns within the data. The following sections outline each AI technique and its applications in healthcare.
Human intelligence abilities such as listening, seeing, smelling, sensing, learning, reasoning and decision-making can be created by machines using various AI intelligence methods. In the world of healthcare, professionals can augment intelligence created by AI to improve the accuracy of diagnosis, predict outcomes, and recommend more effective care paths by detecting hidden and known patterns within the data. The following sections outline each AI technique and its applications in healthcare.
Achieving AI in Medicine with Machine Learning
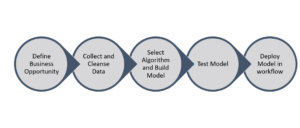
Machine Learning is one of the most commonly used techniques to enable AI in healthcare. It empowers providers by accelerating diagnosis of disease and finding the best treatment options thus improving better outcomes for patients. One of the most commonly discussed machine learning applications is the accurate diagnoses of disease by scanning images and mimicking the skills of radiologists. The following diagram outlines the steps in a typical machine learning process.
 Machine learning is broadly classified into two categories, Supervised and Unsupervised learning. In Supervised machine learning, previously known knowledge with respect to specific data patterns is used to train models. Using supervised machine learning organizations can predict the risk of post-procedure readmission of patients. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms offer the ability to detect patterns by finding similarities within data. One of the exciting examples of unsupervised machine learning is to segment patients by identifying those who respond to certain medication effectively and those who don’t.
Machine learning is broadly classified into two categories, Supervised and Unsupervised learning. In Supervised machine learning, previously known knowledge with respect to specific data patterns is used to train models. Using supervised machine learning organizations can predict the risk of post-procedure readmission of patients. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms offer the ability to detect patterns by finding similarities within data. One of the exciting examples of unsupervised machine learning is to segment patients by identifying those who respond to certain medication effectively and those who don’t.
 Enriching AI with Natural Language Processing
Enriching AI with Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables systems to analyze unstructured data, like physician notes, written in an EMR. With NLP, healthcare organizations can extract specific terms that provide high-value information. For instance, a value of ejection fraction can be extracted from medical notes which will help provide a better assessment of a patient.
In addition, NLP can help improve the accuracy of machine learning models by finding features from notes that can be used as additional dimensions along with structured data.
AI through Computer Vision
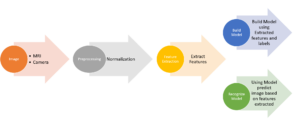
Computer vision is an AI technique that enables machines to have the ability to act like our eyes, it scans images and interprets patterns by extracting features and matching them against similar objects. By combining features extracted from images with other patient data more reach machine learning models can be trained and used to generate intelligence. This will aid providers in making more accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Speech Processing with AI
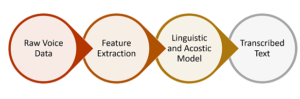
Speech processing is perhaps the most highly adopted AI method in healthcare which is commonly used to record dictations of medical professionals and converting in text format to create digitized medical notes. It is also, called as voice recognition that identifies words by multiple speakers and converts them into machine-readable data.
 According to Reaction Data, 62% of the healthcare organizations use speech recognition tools. With the emergence of voice-enabled devices such as Alexa and Google Home which can interact with algorithms, the possibility of AI predicting healthcare decisions like doctors is becoming reality.
According to Reaction Data, 62% of the healthcare organizations use speech recognition tools. With the emergence of voice-enabled devices such as Alexa and Google Home which can interact with algorithms, the possibility of AI predicting healthcare decisions like doctors is becoming reality.
AI with Expert Systems
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a method that emulates the decision-making of a human expert. Experts systems use rules based on the collective knowledge of many human experts to make a decision for a specific situation. In healthcare, expert systems are used to generate alerts within EMRs as certain conditions are met based on patient data.
Human Expert Knowledge Engineer User
In future, with the ability to have access to systems through smart mobile devices, there will be an explosion of expert-system-based AI application in the healthcare industry. With a focus on self-care and improvements in accuracy and faster diagnosis, these AI applications will be launched at a global scale.
Key AI Adoption Challenges
AI ecosystems have reached a high level of maturity in some organizations, but adoption challenges like shortage of big data infrastructure, lack of data science/AI skillsets, complexity in moving data from traditional systems, and integration of Big Data with AI Algorithms are still challenges. To overcome these challenges, firms must build a comprehensive AI rollout roadmap that sets guidelines for the selecting right use cases, effective technology stack, centralized governance of AI models and strategy for cultivating AI talent. The best approach to build AI skillset is to train internal talent who has domain knowledge of healthcare.
Futureproofing healthcare with AI
AI holds promise to reinvent healthcare by empowering all aspects of operations using augmented intelligence generated by machines. While machines can never replace the human touch, they can and will enable an enormous transformation in Health Care. The cost of not investing in AI has the potential to make organizations irrelevant over the time. AI is equipped with capabilities to reinvent healthcare by augmenting machine intelligence ultimately predicting the best treatment options at the point of care. The most benefit of AI that will drive adoption is the time it can save. Improved speed of decision-making will allow doctors and nurses to spend more time with patient, reduced cost and achieve best in class outcomes for patients.




Pingback: Health Care and the Promise of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)